Abstract
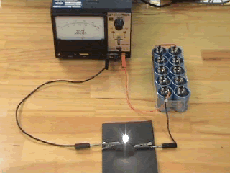
the light bulb.
A capacitor charges and discharges with a long time constant through a light whose brightness indicates the current.
Portable
Yes
Principles Illustrated
Charge and discharge of a capacitor.
Video
Above: Charging the capacitor. Download (right-click and “save link as”): Cap Charge.m4v (4 MB)
Below: Discharging the capacitor. Download (right-click and “save link as”): Cap Discharge.m4v (5 MB)
NCEA & Science Curriculum
PHYS 3.6
Instructions
Charge an electrolytic capacitor through a light bulb. As the capacitor charges the current falls off and the light bulb dims. Then disconnect the power supply and discharge the capacitor through the light bulb. As the capacitor discharges the current again falls off and the bulb dims.

the light bulb.
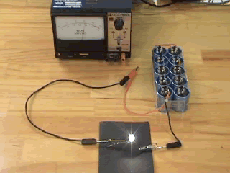
the light bulb.
Safety
Always make SURE that electrolytic capacitors are connected with the correct polarity. Never reverse bias an electrolytic capacitor as it may explode. No kidding.
Individual teachers are responsible for safety in their own classes. Even familiar demonstrations should be practised and safety-checked by individual teachers before they are used in a classroom.
Related Resources
Charge and Discharge a capacitor through an ammeter. Create a spark with a sudden discharge.
Teaching Resources
Would you like to contribute lesson suggestions? Contact us.
References
PIRA 5C30.30, PIRA 5F.30.10
Credits
This teaching resource was developed with support from
The MacDiarmid Institute
Faculty of Science, Victoria University of Wellington
School of Chemical and Physical Sciences, Victoria University of Wellington